Wet blasting
Wet blasting is an environmentally friendly surface treatment to improve the hygiene of stainless steel surfaces. This is highly desirable for certain powder flows in the food sector
Wet blasting and EHEDG
Wet blasting uses a mixture of water and blasting agent. The surface is treated under pressure. This enormously improves the adhesion properties. This makes a stainless steel surface more hygienic than polishing, for example. The process is well suited for devices used in the food industry, such as magnetic separators. Here the demands on the finish are very high. Consider, for example, the processing of powders.
Wet blasting ensures:
- a strong reduction of bacterial growth and microbial contamination in your production process;
- optimum corrosion-resistance;
- significant improvement of the cleanability.
Wet blasting meets industry guidelines
Wet blasting makes magnetic separators ideally suited for the food industry. The magnetic separators from Goudsmit Magnetics comply with all guidelines applicable to this industry, such as EN1672-2, EN ISO14159, 2006/42/EC, (EG)1935/2004 and EHEDG.
The hygienic wet blasting cabin at Goudsmit Magnetics was built by Rössler and was developed in collaboration with TNO (in English: Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research). It is only used for Goudsmit products.
Comparable processes are Purefinish - developed by Rössler - and hygienic surface treatment, developed by The Stainless Solutions Group and Viwateq.
TNO research
Recent research by TNO shows that it is not the surface roughness value (Ra), but rather the soil retention index (SRI) that is the determining factor for how much protein is left behind. This is a key figure for the entire surface area. The lower the SRI, the less adhesion, i.e. the less product is left behind.
According to TNO, certain bacteria adhere better to particularly smooth surfaces (Ra value ≤ 0.2 µm). Therefore, in the hygienic wet blasting process, the 'too smooth' surface is slightly roughened, so that it meets these ideal properties. The final Ra value is approximately 0.3 to 0.6 µm.
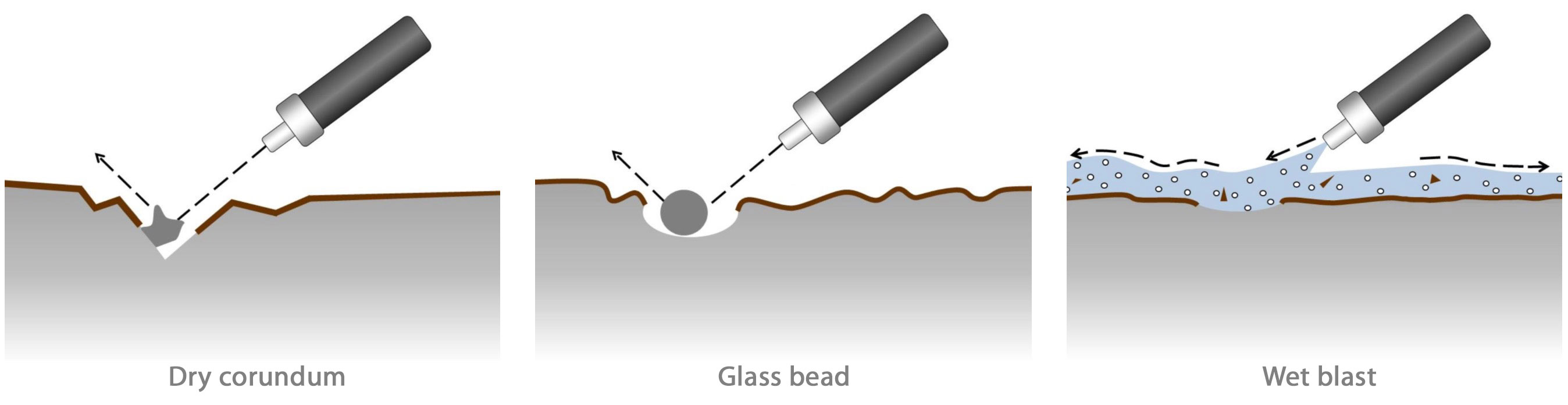
Wet blasting or dry blasting
During dry blasting, with glass beads for example, the impact of the blasting agent actually breaks open the surface. The surface is then clean, but because the resulting surface has an open structure, it is susceptible to scratching, corrosion and adhesion of contaminants.
Wet blasting is a much milder process than dry blasting. Wet blasting uses finer abrasives. The cushioning effect of the water distributes the impact evenly. This ensures a much more even and closed finish. This ‘green’ treatment also does not use any environmentally damaging chemicals.