Electro overband magnets
Search results
Your results in: pages, products and documents
Scroll to see everything. Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try another search term or contact us.
No results found

-
{{filter.Description}}
({{filter.UOMDescription}})








No results found
Your results in: pages, products and documents
Scroll to see everything. Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try another search term or contact us.
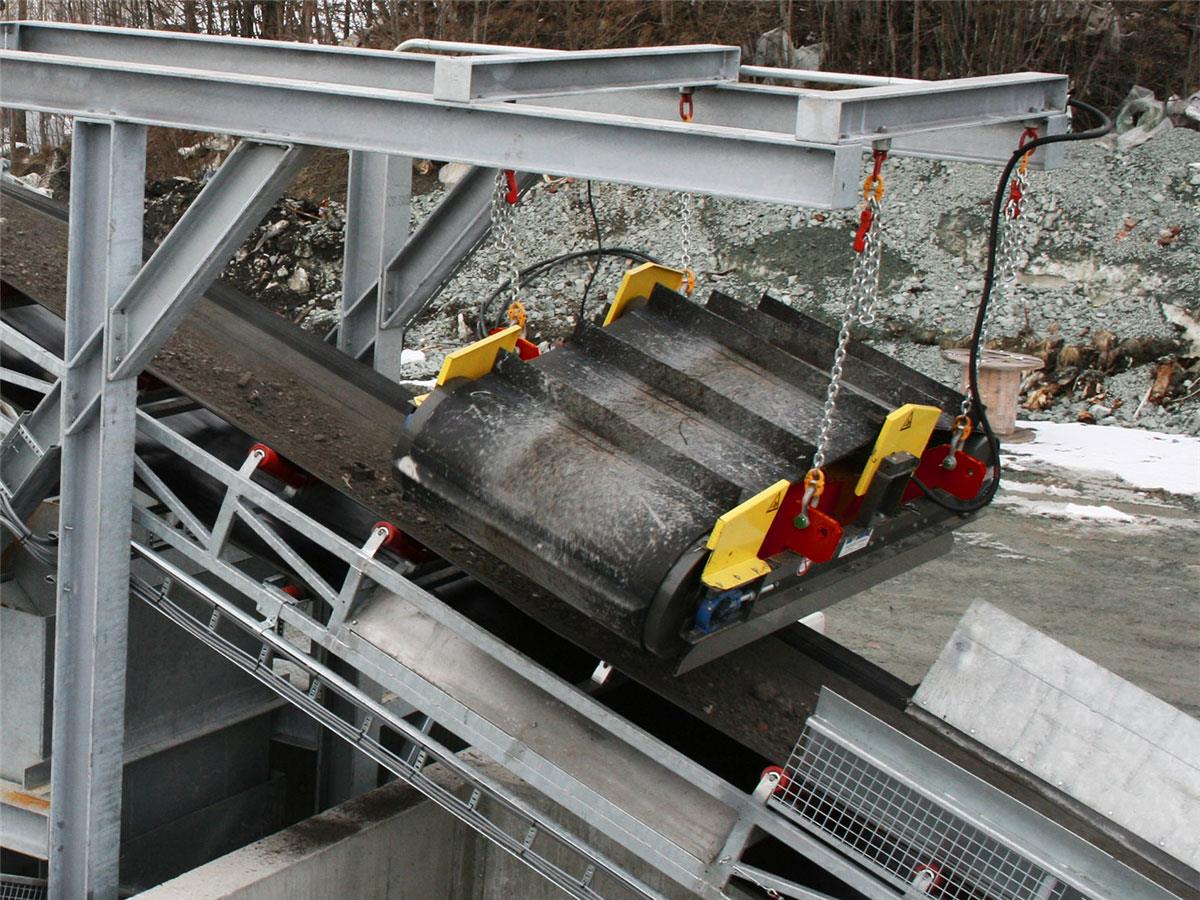
Application of electro overband magnetic separators
An overbelt magnet is suitable for removal or separation of high volumes of iron or steel and hangs above a flat- or trough-shaped conveyor. This type of magnet is self-cleaning and continuously separates Ferrous parts from material streams. The iron removal efficiency of overband magnets ranges from 70 to 90%. This depends on magnet design, product flow and placement. Automatic self-cleaning overbelt magnetic separators are suitable for both the recovery of ferrous parts and the removal of iron impurities.
The electro overband magnet has the deepest holding field and is therefore the most suitable of all the overband magnets for the removal of steel particles from material streams with thick layers. Disadvantages are the higher power consumption and higher weight relative to the permanent overband magnets.

Operation of electro overband magnets
Conveyor belt speed
to remove ferrous or iron parts from a material flow, they must remain in a magnetic field for between approximately 0.3 and 0.5 seconds, where they are magnetized. To achieve maximum separation, it is important to optimally match the size of the magnet block (main pole) and the belt speed. This means that with a narrow overband magnet the conveyor belt beneath it must run at lower capacity (m/s) than with a wider magnet at the same suspension height.
The following formula provides an indication of the maximum conveyor belt speed:
- Maximum conveyor belt speed (b) = block magnet width (a) / 0.3 (sec.)
- Recommended conveyor belt speed (b) = block magnet width (a) / 0.5 (sec.)
.jpg)
Placement of electro overband magnets
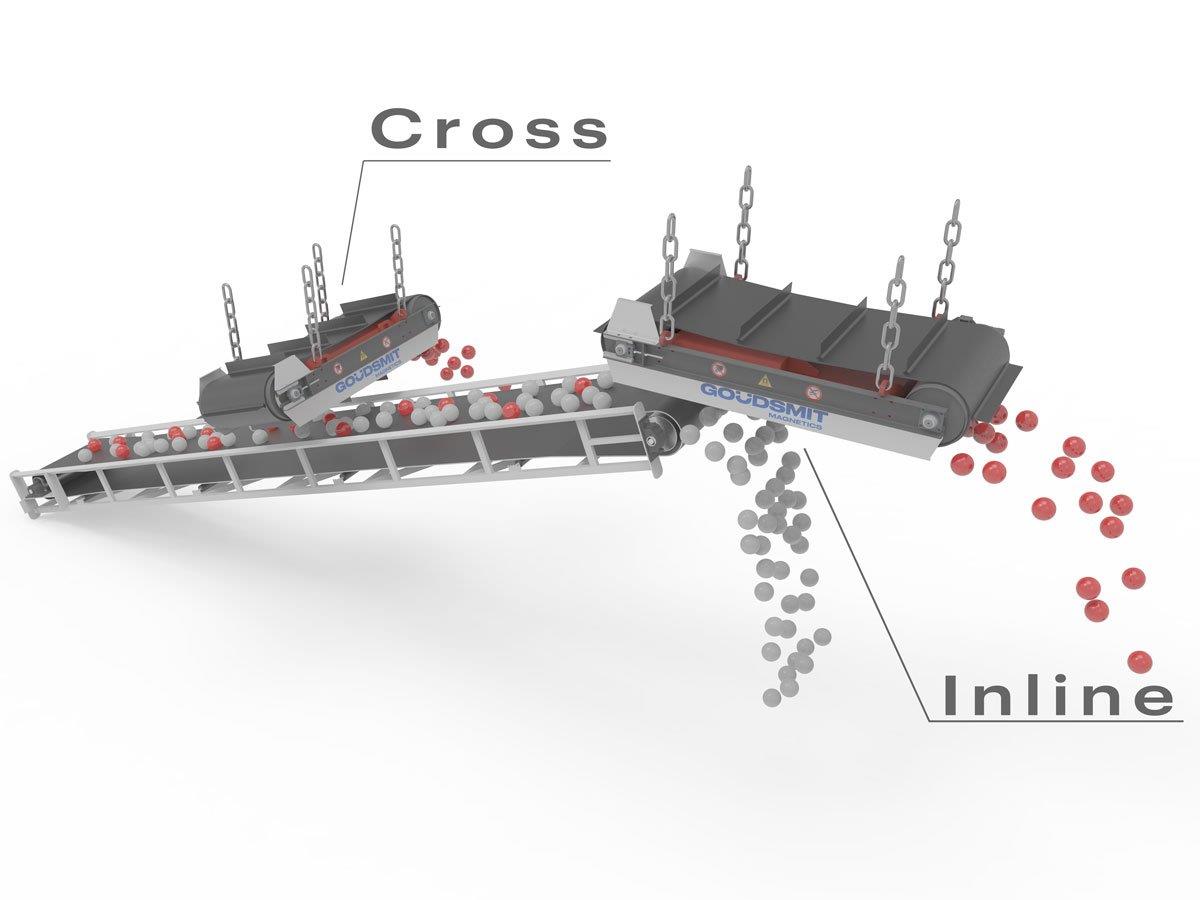
The distance between a magnet and the conveyor belt must be as small as possible. The magnetic force decreases exponentially with increasing distance. There is, however, a minimum distance required so the rubber cleats safely remove all the ferrous parts from the material flow. There are two methods for use/placement of overband magnets: transverse and in-line. Goudsmit has a specific, optimum magnet configuration for both mounting options.
Transverse ('Cross') - cross belt magnetic separator
In practice, transverse placement is most common, because it is easier to install in an existing line. An additional advantage is a ferrous discharge to the side, which from the logistical perspective is easier to process.
‘In-line’
If you have the option to place your overband magnet in line with the conveyor belt, this is always preferred. The advantage of this is that the transported material ‘breaks open’ at the end of the belt (head roller) and is therefore suspended in mid air for several milliseconds. As a result, the magnet can easily pull the ferrous metal out of the product flow.
Non magnetic zone
When positioning the magnet, the construction below the magnet such as the frame, bearing rollers and end rollers must be made of non-magnetic material. This is because steel parts will become magnetized, which will adversely affect the separation performance of the overband magnet. For more information about this: see non-magnetic zone.
.png)


Heavy, robust and very powerful. Electromagnetic overband magnets have a deeply penetrating magnetic field and are therefore suitable for very thick layers. A control box is required. The magnet can be turned off for service or cleaning purposes.